Agriculture, the backbone of civilization, has been at the forefront of technological advancements for centuries. As we step into the 21st century, the integration of technology into agriculture has become more pronounced, leading to significant transformations in farming practices. This essay delves into the impact of agricultural technology on modern farming, highlighting the innovations that have revolutionized the sector and the challenges that still lie ahead.
Innovations in Agricultural Technology
-
Precision Agriculture: One of the most significant advancements in agricultural technology is precision farming. This approach uses information technology to manage field-level data, enabling farmers to apply resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides in a highly targeted manner. GPS-guided machinery and drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns, allowing for real-time decision-making.
-
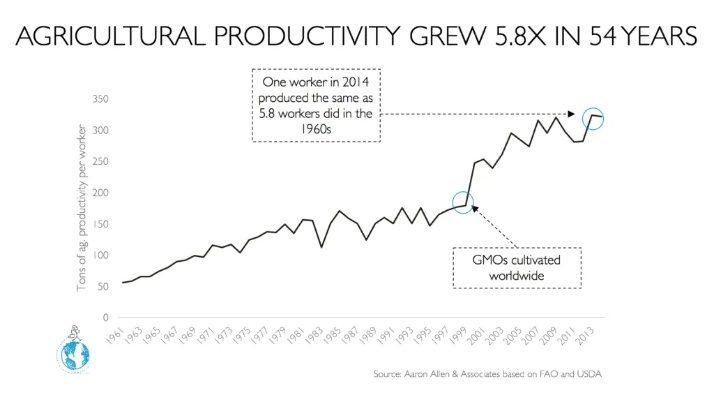
Genetic Modification: Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) have been a controversial yet transformative aspect of modern agriculture. GMOs can be engineered to resist pests, tolerate herbicides, and enhance nutritional content. While there are debates surrounding their safety and environmental impact, GMOs have undeniably increased crop yields and reduced the need for chemical inputs.
-
垂直农业(Vertical Farming): As urbanization encroaches on arable land, vertical farming offers a solution by growing crops in stacked layers, often in controlled environments. This method significantly reduces the land footprint and can be located in urban centers, providing fresh produce to city dwellers while minimizing transportation emissions.
-
机器人技术(Robotics): The use of robots in agriculture is on the rise, with machines capable of planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops. These robots can work around the clock, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency. They also contribute to the reduction of human errors and can be programmed to perform tasks with precision.
-
物联网(Internet of Things, IoT): IoT has made it possible to connect various devices and sensors in the field, collecting and analyzing data to optimize farming practices. This connectivity allows for remote monitoring and management of crops, machinery, and resources, leading to more sustainable and efficient farming.
-
数据分析和人工智能(Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence, AI): AI and machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of data to predict crop diseases, optimize irrigation systems, and forecast market trends. These insights help farmers make informed decisions, reducing waste and increasing profitability.
Challenges in Agricultural Technology
Despite the numerous benefits, the adoption of agricultural technology also faces several challenges:
-
成本问题(Cost): Advanced agricultural technologies can be expensive, making them inaccessible to small-scale farmers who constitute a significant portion of the global farming community.
-
技术接受度(Technological Acceptance): There is often resistance to change, especially among traditional farmers who may be skeptical of new technologies or lack the necessary skills to operate them.
-
监管和政策(Regulation and Policy): The regulatory environment surrounding agricultural technology, particularly GMOs and data privacy, can be complex and vary greatly between countries, hindering the widespread adoption of these innovations.
-
环境影响(Environmental Impact): While many technologies aim to reduce environmental impact, concerns remain about their long-term effects on biodiversity, soil health, and water resources.
-
劳动力转移(Labor Displacement): The automation of farming processes may lead to job losses in the agricultural sector, requiring new skills and retraining for those affected.
In conclusion, the impact of agricultural technology on modern farming is profound, offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges facing the sector, such as food security and sustainability. However, the path to widespread adoption is not without obstacles. It requires a balanced approach that addresses the economic, social, and environmental aspects of technology integration. As a tech expert, I believe that continued research, education, and collaboration among stakeholders are essential to overcoming these challenges and harnessing the full potential of agricultural technology for the benefit of all.